Tough Resins
Introduction to Tough Resins for 3D Printing
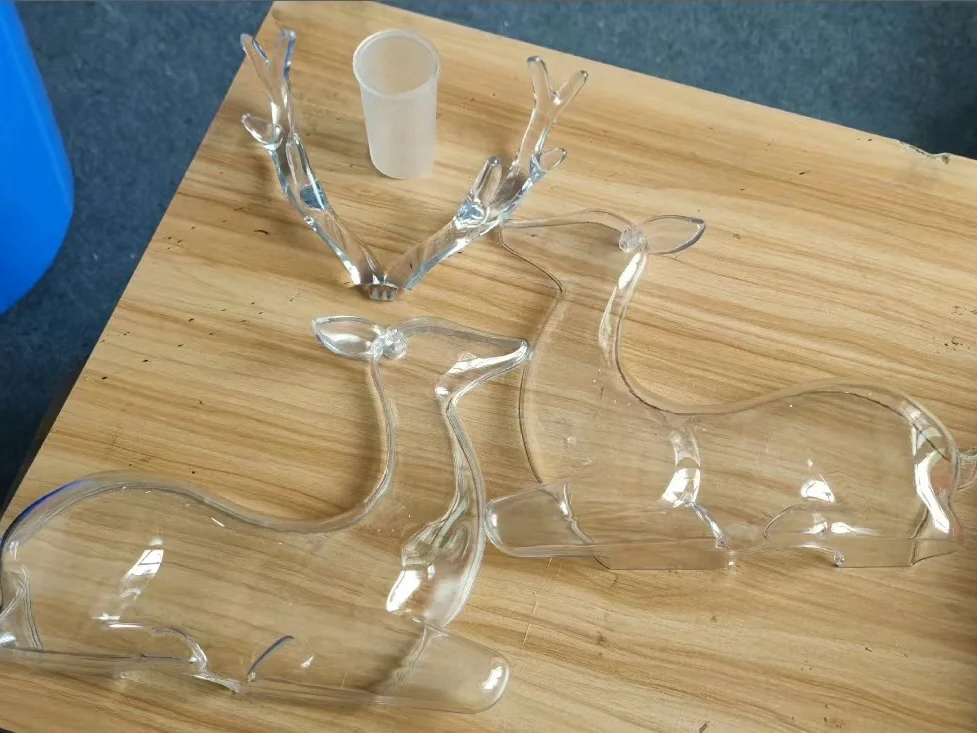
Tough resins are engineering-grade photopolymers formulated to deliver a balance of strength, impact resistance, and moderate flexibility. These materials simulate the mechanical behavior of ABS or polypropylene, making them ideal for functional prototypes, enclosures, snap-fit assemblies, and impact-prone parts.
Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) are the preferred processes for tough resins, enabling ±0.05 mm accuracy with high-resolution detail and improved fracture toughness over standard resins.
International Equivalent Grades of Tough Resin
Grade Type | Resin Code | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
Tough Resin | Engineering R1600 | Snap-fits, enclosures, brackets |
Durable Resin | Engineering R1800 | Hinge parts, wear-resistant shells |
ISO Standard | ISO 527 | Structural resin measurements |
ASTM Standard | D638 | Mechanical property testing |
Comprehensive Properties of Tough Resins
Property Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Density | 1.12–1.15 g/cm³ |
UV Curing Wavelength | 405 nm | |
Mechanical | Tensile Strength | 50–55 MPa |
Modulus of Elasticity | 1,800–2,000 MPa | |
Elongation at Break | 20–30% | |
Impact Strength (Notched Izod) | 45–55 J/m | |
Thermal | Heat Deflection Temperature | 45–60°C |
Suitable 3D Printing Processes for Tough Resins
Process | Typical Density Achieved | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Dimensional Accuracy | Application Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥99% | 3–6 µm | ±0.05 mm | Ideal for enclosures, load-bearing prototypes, and precision mechanical components | |
≥99% | 4–8 µm | ±0.05 mm | Best for detailed parts requiring mechanical performance and dimensional reliability |
Selection Criteria for Tough Resin 3D Printing
Impact Resistance: Tough resin is engineered to absorb impact and resist fracture, ideal for drop-tested prototypes or mechanical test parts.
Functional Strength: Similar to ABS, it supports mechanical loads and limited deformation, useful for brackets, snap-fits, and assemblies.
Detail and Surface Finish: Delivers fine edge detail and matte surface finish with little post-processing—ideal for both internal and customer-facing parts.
Printability and Stability: Designed for reliable printing with minimal shrinkage and cracking, ensuring consistency across parts with complex geometries.
Essential Post-Processing Methods for Tough Resin Parts
UV Post-Curing: Necessary to reach full strength; cure at 405 nm for 30–60 minutes depending on part thickness and geometry.
IPA Rinsing and Support Removal: Remove excess resin using isopropyl alcohol, followed by support detachment and air or UV drying.
Light Sanding and Polishing: Improves aesthetics and feel for consumer-grade housings or product interface points.
Adhesive or Mechanical Assembly: Parts can be bonded using epoxy or press-fit for assembly into test fixtures or housings.
Challenges and Solutions in Tough Resin 3D Printing
UV Brittleness from Overcuring: Avoid excessive post-curing beyond spec; monitor time and intensity to preserve ductility and prevent premature embrittlement.
Humidity and Storage Stability: Store resin in sealed containers and print parts in humidity-controlled environments to reduce print failures and degradation.
Part Warping in Large Models: Design large flat parts with radii or ribs to reduce stress. Orient builds to minimize overhangs and reduce peel forces.
Applications and Industry Case Studies
Tough resins are widely used in:
Consumer Products: Snap-fit prototypes, device housings, and testable product casings.
Manufacturing Tools: Assembly jigs, fixtures, brackets, and temporary tooling components.
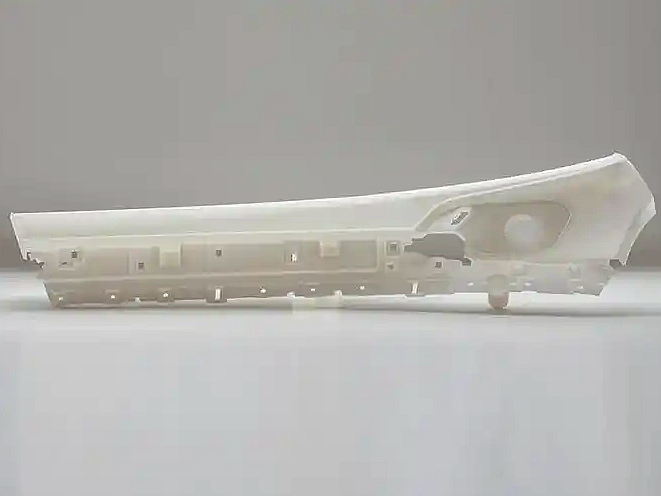
Automotive: Lightweight interior trim, mounting brackets, and accessory prototypes.
Electronics: Cable guides, connector housings, and functional testing hardware.
Case Study: An electronics manufacturer used tough resin SLA to prototype a multi-part enclosure with snap-fit interfaces. The parts withstood 200+ open/close cycles and passed dimensional validation with ±0.05 mm tolerance.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does tough resin compare to ABS or PLA in impact strength and flexibility?
Is tough resin suitable for snap-fit components and dynamic mechanical testing?
What are the ideal curing and post-processing steps for tough resin parts?
How accurate are tough resin parts for toleranced mechanical assemblies?
What industries commonly use tough resin for rapid prototyping and low-volume testing?