Standard Resins
Introduction to Standard Resins for 3D Printing
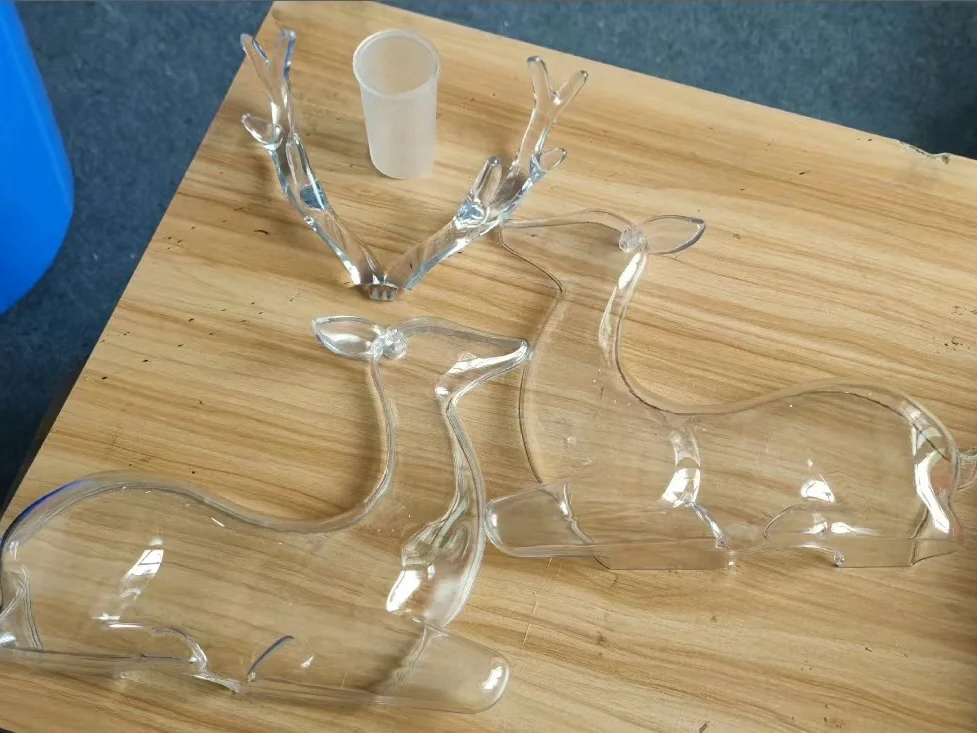
Standard resins are photopolymer materials used in SLA, DLP, and LCD 3D printing that provide high-resolution surface finishes and excellent dimensional accuracy. These resins are ideal for visual prototypes, models, low-load components, and parts requiring fine detail and smooth appearance.
Stereolithography (SLA) and Digital Light Processing (DLP) are preferred technologies for printing standard resins, producing smooth-surfaced parts with ±0.05 mm accuracy, ideal for early-stage product validation and detailed display models.
International Equivalent Grades of Standard Resins
Standard | Grade Code | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
ISO | ISO 527 | General photopolymer resins |
ASTM | D638 | Rigid modeling resins |
China | GB/T 1634.2 | 光敏树脂 (Light-sensitive resin) |
Comprehensive Properties of Standard Resins
Property Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Density | 1.10–1.15 g/cm³ |
Cure Wavelength | 405 nm | |
Mechanical | Tensile Strength | 40–60 MPa |
Elastic Modulus | 2,000–2,500 MPa | |
Elongation at Break | 5–10% | |
Shore Hardness | 85–90 Shore D | |
Other | Surface Finish | High Smoothness |
Suitable 3D Printing Processes for Standard Resins
Process | Typical Density Achieved | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Dimensional Accuracy | Application Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥99% | 2–6 µm | ±0.05 mm | Best for visual models, prototypes, and cosmetic components | |
≥99% | 4–8 µm | ±0.05 mm | Ideal for detailed parts with sharp edges and aesthetic features |
Selection Criteria for Standard Resin 3D Printing
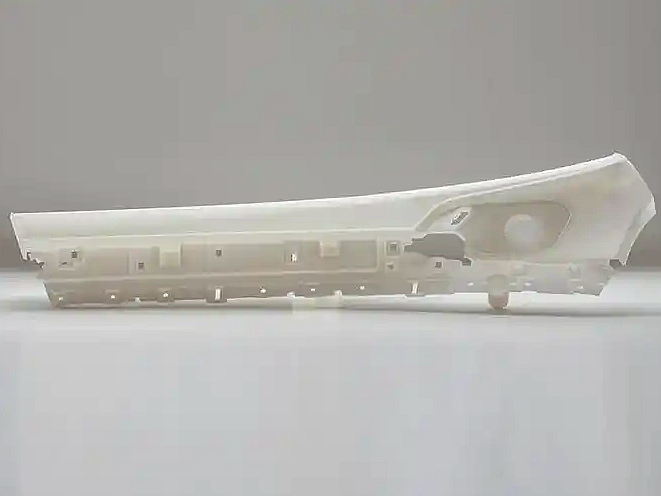
Visual Appearance: Standard resins produce smooth surfaces with high edge fidelity, ideal for presentation models, concept evaluation, and fit testing.
Detail Resolution: Support features as small as 0.2 mm, making them suitable for miniatures, decorative parts, and design verification.
Brittleness Consideration: Standard resins are rigid but brittle—avoid functional load-bearing or impact applications unless switching to engineering-grade resins.
Color and Finish Options: Available in gray, white, black, or transparent options. Compatible with painting and coating for cosmetic finishing.
Essential Post-Processing Methods for Standard Resin Parts
UV Curing: Post-curing at 405 nm for 15–30 minutes ensures full polymerization, improving mechanical performance and long-term stability.
Washing and Drying: Use isopropyl alcohol (IPA) or ethanol to remove uncured resin, followed by air or UV drying.
Sanding and Painting: Post-finish to enhance appearance, especially on display models, housings, or pre-production mock-ups.
Assembly or Bonding: Use CA adhesives or light sanding on joining surfaces to integrate printed parts into larger builds or visual assemblies.
Challenges and Solutions in Standard Resin 3D Printing
Brittleness in Thin Parts: Avoid unsupported thin sections or switch to a tough resin for durability. Increase wall thickness to ≥1.5 mm.
UV Aging Over Time: Store finished parts away from UV exposure to prevent color shifts or surface chalking; apply clear UV coating for added protection.
Print Orientation Effects: Orient parts to reduce visible layer lines on display surfaces and improve structural support during curing.
Applications and Industry Case Studies
Standard resin is widely used in:
Product Development: Concept models, ergonomic prototypes, and housing evaluation.
Consumer Goods: Decorative accessories, cosmetics packaging, and visual prototypes.
Education & Research: Study models, anatomical displays, and architectural miniatures.
Marketing & Display: Presentation parts, mock-ups, and demo product models.
Case Study: A medical equipment manufacturer used SLA standard resin to develop a pre-market housing prototype. With ±0.05 mm precision and polished finishing, the part allowed rapid validation in form, size, and user interface before tooling investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the dimensional tolerances and surface resolution of standard resin 3D prints?
Are standard resins suitable for functional or load-bearing parts?
What post-processing steps are needed for cosmetic presentation parts?
How do SLA and DLP differ in printing standard resin materials?
What industries typically use standard resin for pre-production or design validation?