Can Binder Jetting produce copper parts, and what are its advantages?
Can Binder Jetting Produce Copper Parts, and What Are Its Advantages?
Feasibility of Copper in Binder Jetting
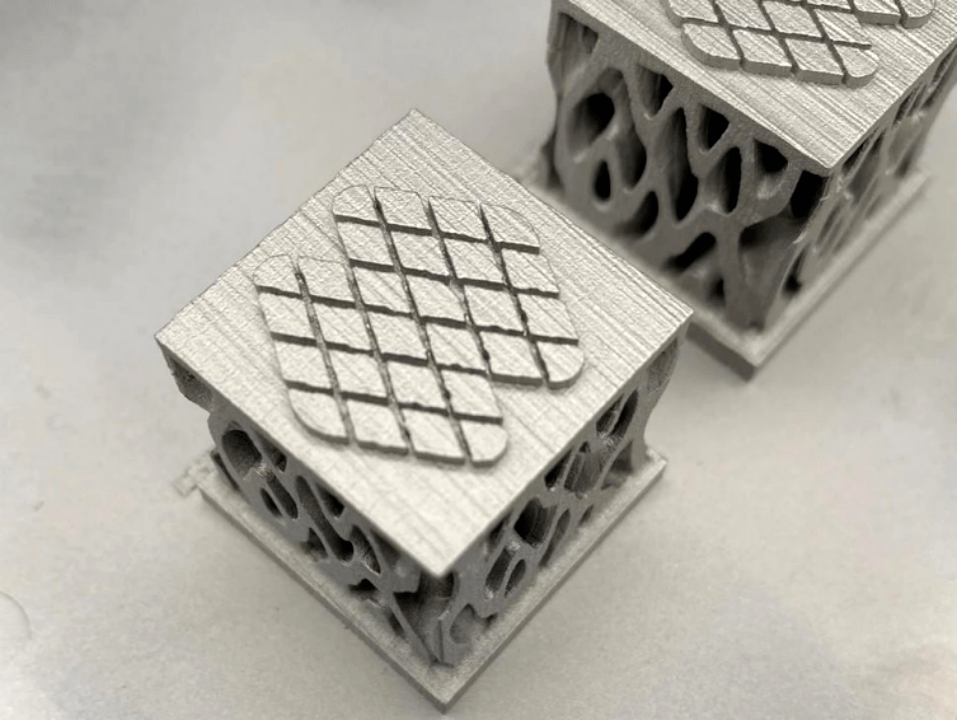
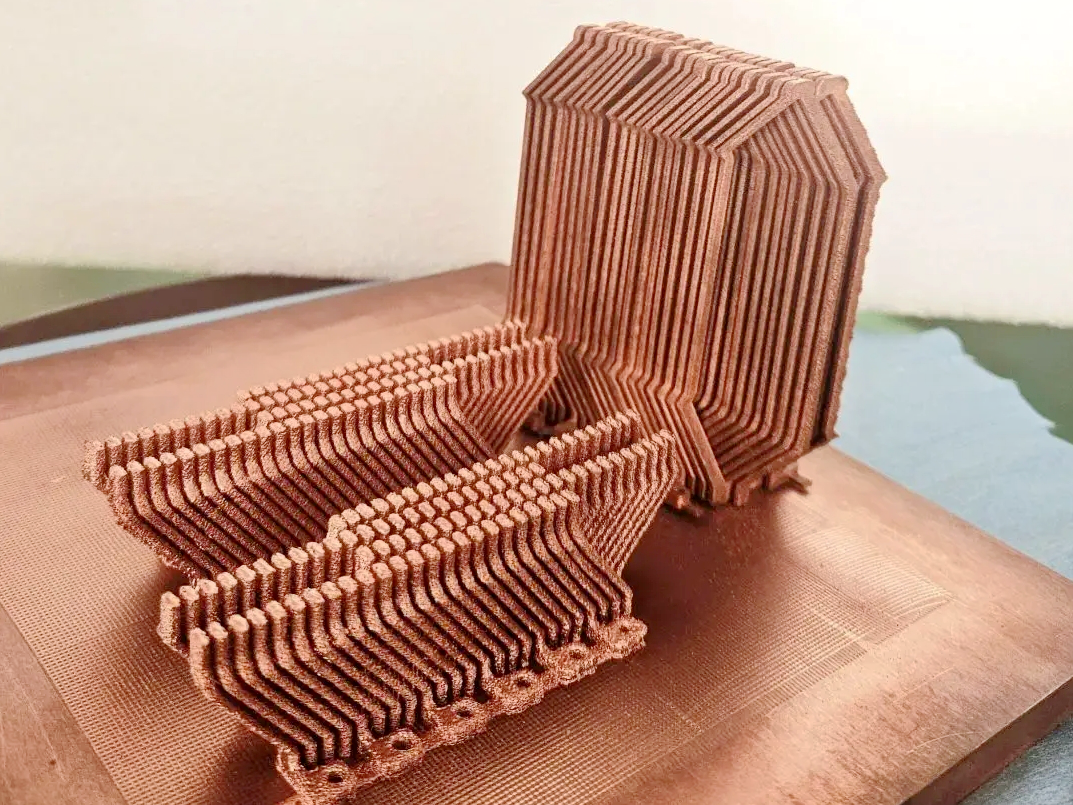
Yes, Binder Jetting is a highly effective method for producing copper parts, especially when high electrical or thermal conductivity is required at scale. Copper grades such as Copper C101, Copper C110, and CuCr1Zr can be printed using this technology. After printing, parts undergo debinding and sintering to achieve densities above 90%, with conductivity suitable for industrial, electronics, and heat management applications.
Key Advantages of Binder Jetting for Copper
1. High Throughput and Cost Efficiency
Binder Jetting builds entire layers at once, enabling rapid print speeds ideal for batch production. It is significantly faster and more scalable than laser-based copper printing and eliminates the need for support structures, reducing post-processing time and cost.
2. Excellent Design Flexibility
The process allows for the creation of complex internal geometries, thin walls, and nested assemblies without supports. This is beneficial for printing lightweight heat exchangers, bus bars, and electronic housings with integrated cooling channels.
3. Lower Energy Consumption
Since Binder Jetting doesn’t rely on high-energy lasers or melting during printing, it consumes less energy during the build phase. Final densification is achieved through sintering, which can be optimized for batch processing.
4. Material Reusability and Reduced Waste
Unused powder remains unbound and can be recycled with minimal degradation, improving overall material efficiency—important when using high-purity copper powders.
Customer-Oriented Solutions and Services
We support Binder Jetting of copper with:
3D Printing Technologies:
Utilize our Binder Jetting process for scalable, cost-effective production of Copper Alloy 3D Printing components.
Copper Material Options:
Industry Applications and Finishing:
Explore use cases in consumer electronics, energy systems, and automotive, supported by surface treatment and CNC machining for functional end-use parts.