How does Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) differ from Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
How Does Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) Differ from Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
Process Mechanism and Material Compatibility
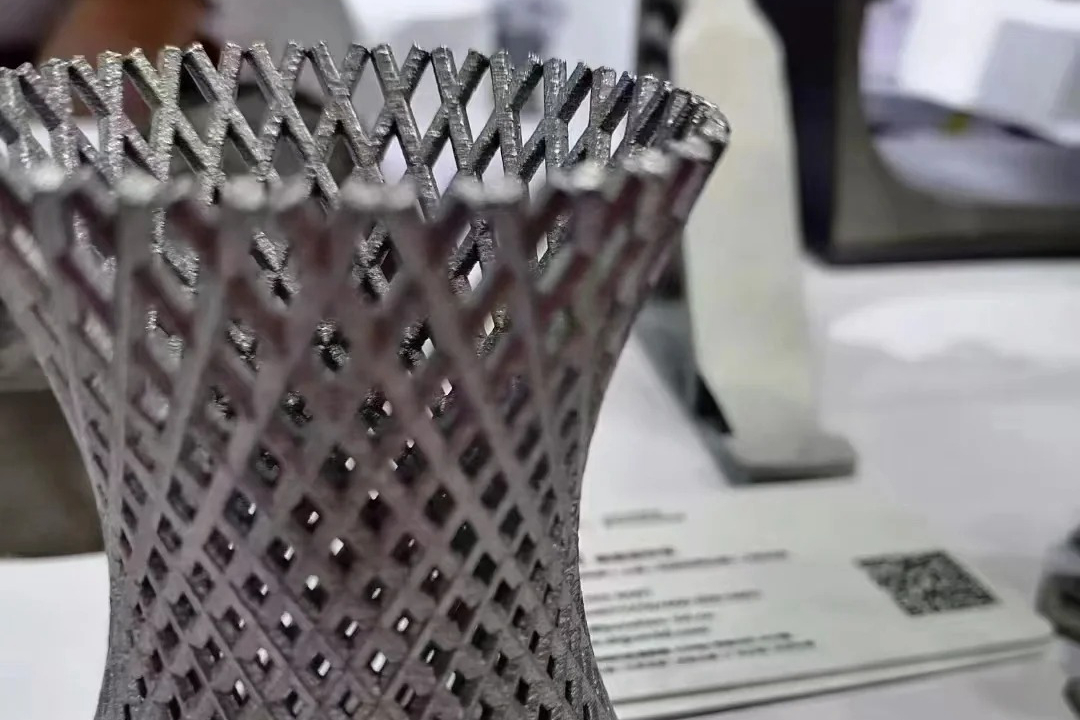
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) are both powder bed fusion technologies, but they differ fundamentally in material use and sintering mechanics.
DMLS utilizes a high-energy laser to fuse metal powders, forming near-full-density metal parts.
SLS applies thermal energy to sinter plastic powders without melting them entirely, producing durable but lower-density thermoplastic parts.
DMLS is suitable for metals such as Inconel 625, Ti-6Al-4V, and Stainless Steel SUS316L, while SLS commonly uses thermoplastics like Nylon (PA) and TPU.
Mechanical and Thermal Performance
DMLS parts achieve densities exceeding 99.5%, offering mechanical properties comparable to forged metals:
Tensile strength for Ti-6Al-4V: ~950 MPa
Heat resistance: up to 600°C depending on material
SLS parts are lower in density but provide functional strength and durability for plastics:
Tensile strength for Nylon PA12: ~48 MPa
Heat resistance: generally below 180°C
Thus, DMLS is suitable for aerospace, medical, and tooling components, while SLS fits consumer products, housings, and flexible prototypes.
Accuracy, Surface Quality, and Support Requirements
DMLS produces parts with complex internal geometries and superior mechanical properties but requires:
Support structures for overhangs
Post-processing such as heat treatment and CNC machining
SLS enables support-free printing of nested geometries due to the surrounding powder bed and typically needs minimal post-processing, limited to finishing or dyeing.
Customer-Oriented Solutions and Services
To support different production needs, we provide:
3D Printing Technologies:
Learn about Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS).
Material Options:
Choose from high-performance metal powders and engineering-grade plastics suited for your application's mechanical and thermal demands.
Post-Processing Services:
Improve dimensional accuracy and surface finish through CNC machining, HIP, or polishing.