Can Binder Jetting produce stainless steel parts, and what are its advantages?
Can Binder Jetting Produce Stainless Steel Parts, and What Are Its Advantages?
Feasibility of Stainless Steel in Binder Jetting
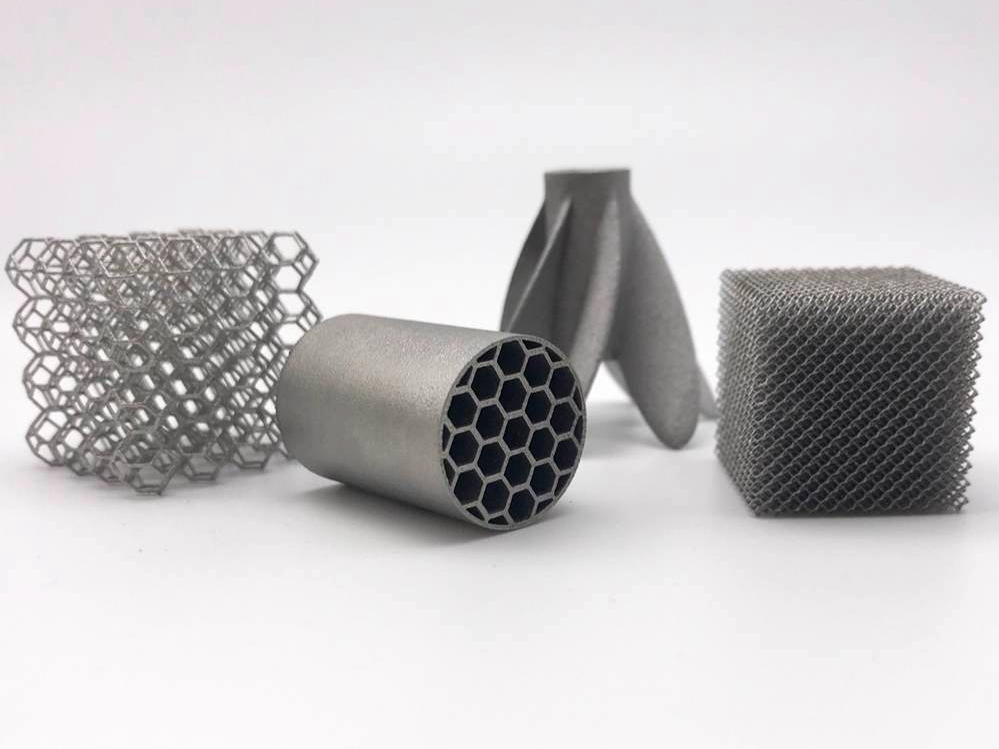
Yes, Binder Jetting is well-suited for producing stainless steel components, especially for medium- to high-volume applications. This technology selectively deposits a liquid binder onto a bed of stainless steel powder to form green parts, which are then cured, debound, and sintered to achieve final density and strength. Grades such as SUS316L, SUS304, and 17-4 PH are commonly used in Binder Jetting for a wide range of industrial, medical, and consumer applications.
Advantages of Binder Jetting for Stainless Steel Parts
1. High Throughput and Productivity
Binder Jetting builds entire layers at once, rather than scanning line-by-line with a laser. This enables significantly faster build times and is ideal for batch production of small-to-medium-sized parts.
2. No Support Structures Required
Unlike melting-based processes, the surrounding powder in Binder Jetting supports the part during printing. This allows complex geometries, internal cavities, and part nesting without design restrictions or additional removal steps.
3. Cost Efficiency
Binder Jetting uses lower energy input and allows for high material reuse. Combined with scalable print platforms and sintering furnaces, it offers a lower cost-per-part, especially for high-volume stainless steel production.
4. Good Surface Finish and Detail
Binder Jetting achieves surface roughness in the range of Ra 6–12 µm in the as-sintered state and can be further improved with surface treatment or polishing, making it suitable for consumer-facing or aesthetic applications.
Post-Processing and Mechanical Properties
To reach near-wrought properties, Binder Jetting stainless steel parts often undergo:
Sintering to achieve 95–98% density
Optional Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) for further densification and fatigue resistance
CNC machining for critical tolerances and assembly fits
Customer-Oriented Solutions and Services
To meet diverse stainless steel part needs using Binder Jetting, we offer:
3D Printing Technologies:
Access Binder Jetting under our broader Stainless Steel 3D Printing capabilities for high-throughput production.
Stainless Steel Material Options:
Industry Applications and Finishing:
Discover stainless solutions for medical, consumer electronics, and industrial components, enhanced by surface treatment and precision machining.