Stainless Steel SUS304
SUS630 / 17-4 PH 3D Printing Materials Introduction
Stainless Steel SUS630 / 17-4 PH is a precipitation-hardened martensitic stainless steel offering high strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance. It maintains structural stability and mechanical performance at temperatures up to 315°C, making it ideal for demanding engineering environments.
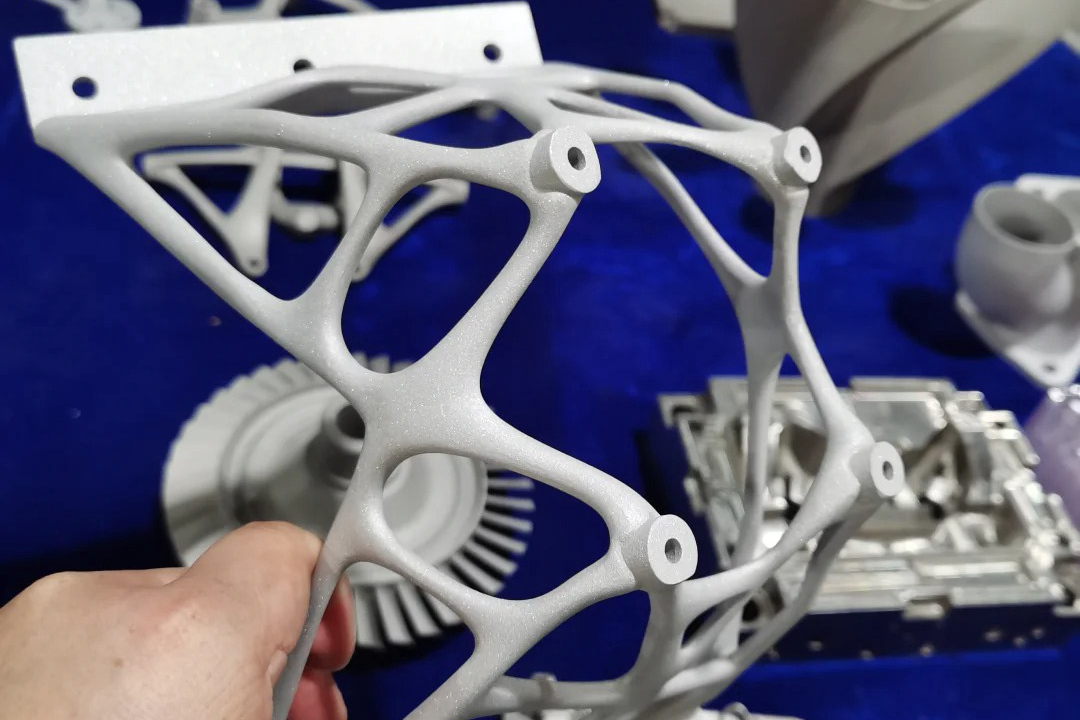
With stainless steel 3D printing, SUS630 enables rapid production of load-bearing parts with tight tolerances, particularly for aerospace, tooling, and industrial machinery applications.
SUS630 / 17-4 PH Similar Grades Table
Country/Region | Standard | Grade or Designation |
|---|---|---|
USA | ASTM | 17-4 PH |
UNS | Unified | S17400 |
ISO | International | X5CrNiCuNb16-4 |
China | GB/T | 0Cr17Ni4Cu4Nb |
Germany | DIN/W.Nr. | 1.4542 |
SUS630 / 17-4 PH Comprehensive Properties Table
Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical Properties | Density | 7.75 g/cm³ |
Melting Point | 1400–1440°C | |
Thermal Conductivity (100°C) | 17.0 W/(m·K) | |
Electrical Resistivity | 80 µΩ·cm | |
Chemical Composition (%) | Iron (Fe) | Balance |
Chromium (Cr) | 15.0–17.5 | |
Nickel (Ni) | 3.0–5.0 | |
Copper (Cu) | 3.0–5.0 | |
Niobium (Nb) + Tantalum (Ta) | 0.15–0.45 | |
Mechanical Properties | Tensile Strength (H900) | ≥1310 MPa |
Yield Strength (0.2%) (H900) | ≥1170 MPa | |
Elongation at Break (H900) | ≥10% | |
Hardness (HRC) | 38–44 | |
Modulus of Elasticity | 200 GPa |
3D Printing Technology of SUS630 / 17-4 PH
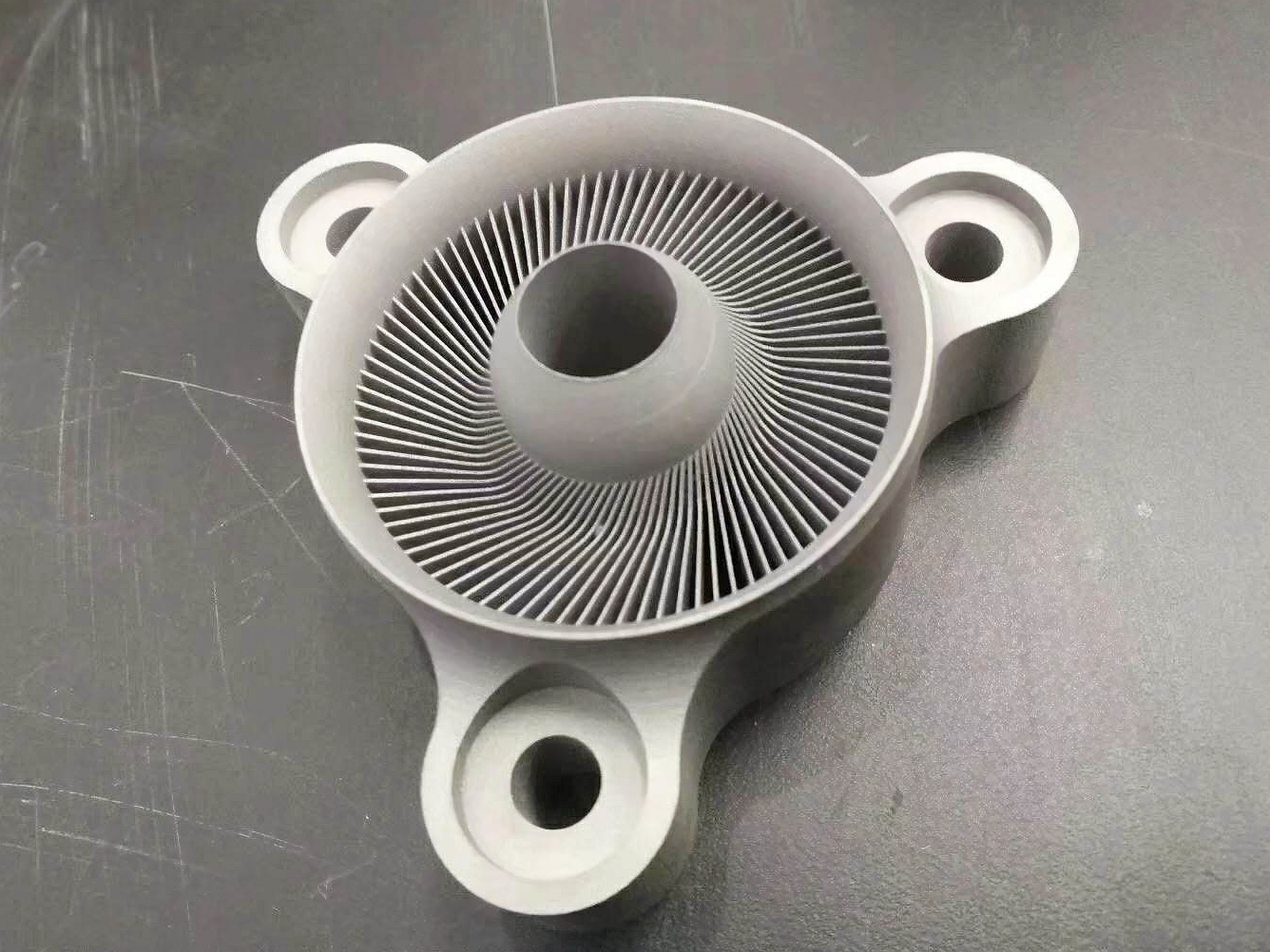
SUS630 is suitable for Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), and Binder Jetting. These processes enable complex part geometries with excellent dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength after aging.
Applicable Process Table
Technology | Precision | Surface Quality | Mechanical Properties | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
SLM | ±0.05–0.2 mm | Excellent | Excellent (post-aged) | Aerospace, Tooling Components |
DMLS | ±0.05–0.2 mm | Very Good | Excellent | Industrial and Structural Parts |
Binder Jetting | ±0.1–0.3 mm | Moderate | Good (post-HIP) | Fixtures, Casings, Large Components |
SUS630 / 17-4 PH 3D Printing Process Selection Principles
SLM is preferred when high mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and geometric complexity are required. It delivers post-aging tensile strength ≥1300 MPa and dimensional precision of ±0.05 mm.
DMLS offers similar performance and is ideal for precision-engineered parts requiring uniform microstructure and excellent fatigue resistance.
Binder Jetting suits large parts with moderate load requirements, where sintering and HIP enhance final density and strength.
SUS630 / 17-4 PH 3D Printing Key Challenges and Solutions
Residual stress and distortion can occur due to martensitic phase transformation. Heat treatment at 480–620°C (H900–H1150) relieves stress and stabilizes microstructure.
Porosity and lack of fusion defects are common in high-strength parts. Using optimized scan strategies, laser power (~300–400 W), and layer thickness (~30 µm) ensures >99.8% density.
Surface finish (Ra 6–15 µm) may be insufficient for sealing or wear interfaces. CNC machining and electropolishing reduce roughness to Ra <1.6 µm.
Hardness and wear performance are enhanced through aging treatments (H900–H1150) to achieve target mechanical profiles across various load-bearing applications.
Typical Post-Processing for SUS630 / 17-4 PH 3D Printed Parts
Aging Heat Treatment at H900–H1150 tempers martensite and maximizes strength and hardness. CNC Machining ensures tight tolerances and surface finishes for high-precision fits and interfaces. Electropolishing enhances corrosion resistance and surface quality in hydraulic and marine environments. Passivation improves long-term corrosion performance by removing free iron and stabilizing passive layers.
Industry Application Scenarios and Cases
SUS630 / 17-4 PH is widely used in:
Aerospace and Aviation: Turbine brackets, housings, and fasteners needing strength and corrosion resistance.
Tooling and Dies: Cores, inserts, and precision dies with high wear and dimensional requirements.
Oil & Gas and Energy: Valve components, pump shafts, and flanges operating under pressure and corrosive fluids.
Defense and Marine: Mounting structures and sealing interfaces with high hardness and fatigue strength.
A recent aerospace case study demonstrated the use of 3D printed 17-4 PH brackets with post-H900 treatment, achieving weight reduction of 35% and mechanical performance exceeding forged equivalents.
FAQs
What are the benefits of using SUS630 / 17-4 PH in 3D printing over conventional alloys?
Which post-processing treatments are required for 17-4 PH stainless steel?
How does heat treatment affect the performance of 3D printed 17-4 PH parts?
What is the typical hardness range of 17-4 PH after aging?
In which industries is SUS630 commonly used for additive manufacturing?