Scalmalloy®
Introduction to Scalmalloy® for 3D Printing
Scalmalloy® is a patented high-performance aluminum-magnesium-scandium alloy developed by APWORKS and Airbus Group specifically for additive manufacturing. It offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, fatigue resistance, and corrosion resistance, with mechanical properties that surpass traditional aerospace aluminum alloys like 6061, 7075, and 2024.
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) is the exclusive process for printing Scalmalloy®, achieving near-wrought strength with ≥99.5% part density and dimensional tolerances of ±0.1 mm. The alloy is qualified for structural aerospace components and lightweight, fatigue-loaded designs.
International Equivalent Grades of Scalmalloy®
Region | Grade Code | Equivalent Standards |
|---|---|---|
Global | Scalmalloy® | AlMgSc (proprietary) |
USA | – | No UNS or AA equivalent |
Europe | – | Aerospace-only proprietary alloy |
Aerospace | AMS Spec In Development | Qualified in Airbus platforms |
Comprehensive Properties of Scalmalloy® (3D Printed)
Property Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Density | 2.67 g/cm³ |
Thermal Conductivity | ~120–130 W/m·K | |
Mechanical | Tensile Strength (as-built) | 460–520 MPa |
Yield Strength | 340–380 MPa | |
Elongation at Break | 8–12% | |
Fatigue Strength (10⁷ cycles) | ~200 MPa | |
Thermal | Operating Temp. Range | Up to 180°C |
Suitable 3D Printing Processes for Scalmalloy®
Process | Typical Density Achieved | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Dimensional Accuracy | Application Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥99.5% | 8–12 µm | ±0.1 mm | Aerospace brackets, UAV structures, and fatigue-loaded lightweight frames |
Selection Criteria for Scalmalloy® 3D Printing
Highest Strength of Any AM Aluminum Alloy: Outperforms 7075 and 2024 in tensile and yield strength while maintaining superior fatigue resistance.
Weldability and Crack Resistance: Scandium content dramatically reduces hot cracking and improves solidification, enabling reliable large prints.
Fatigue and Vibration Resistance: Validated in flight-critical and cyclic-load parts; ideal for drones, space structures, and dynamic mechanical systems.
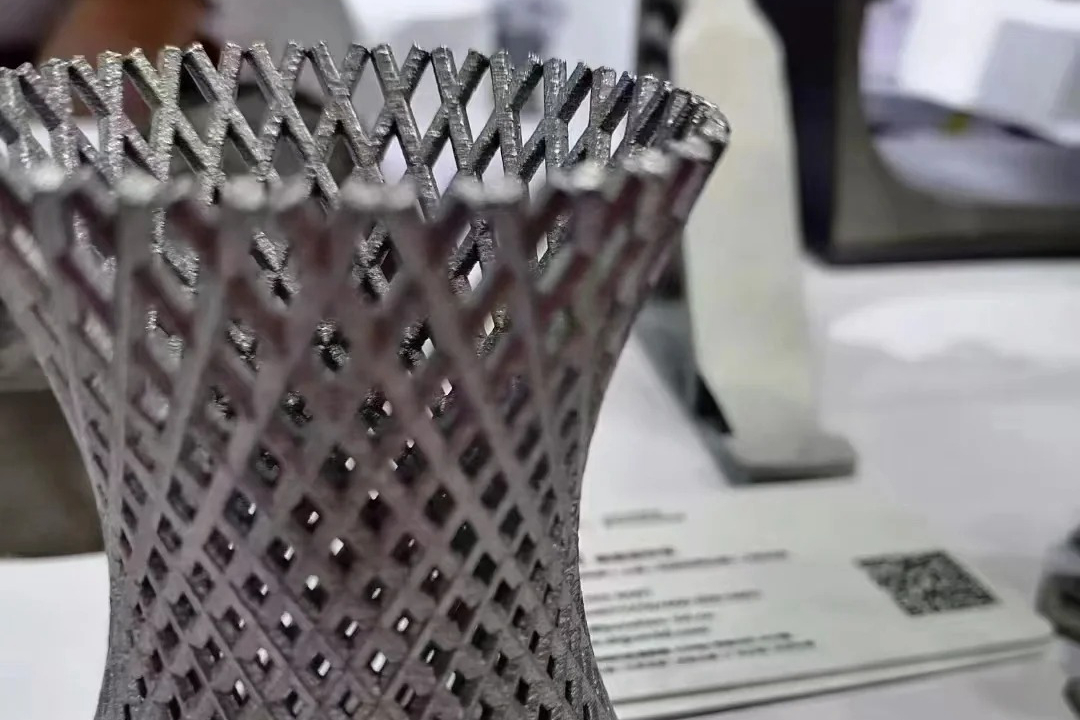
Lightweight Design Freedom: Supports advanced lattice structures and topology-optimized designs in weight-sensitive applications.
Essential Post-Processing Methods for Scalmalloy® Parts
Aging Treatment (Heat Treatment Optional): Scalmalloy® is used in the as-built condition, but artificial aging can further tune mechanical properties when required.
CNC Machining: For toleranced surfaces and interfaces—threads, bearing bores, and sealing planes.
Surface Finishing: Anodizing or chromate conversion improves corrosion resistance and cosmetic finish for aerospace use.
Shot Peening (Fatigue Enhancement): Improves fatigue strength further for parts subjected to dynamic loading.
Challenges and Solutions in Scalmalloy® 3D Printing
Material Licensing and Powder Availability: Use only qualified machines and powder suppliers. Printing requires parameters licensed from APWORKS.
High Cost vs Conventional Aluminum: Best suited for critical, high-value parts where performance justifies cost (e.g., flight hardware, race vehicles).
Thermal Distortion in Large Builds: Apply preheating, build plate anchoring, and optimized orientation to prevent warping in long, thin parts.
Applications and Industry Case Studies
Scalmalloy® is widely used in:
Aerospace: Satellite brackets, wing ribs, airframe structures, UAV frames, and launch system mounts.
Defense: Lightweight deployable structures, armored drone components, and sensor housings.
Motorsports: Impact-critical brackets, chassis components, and suspension links.
Robotics & Drones: Structural frames, drone arms, and fatigue-loaded moving parts.
Case Study: Airbus used Scalmalloy® to produce structural brackets for commercial aircraft. The 3D printed parts reduced weight by 45% over machined titanium and passed all fatigue, vibration, and flight qualification tests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What makes Scalmalloy® superior to 7075 or 2024 in 3D printing?
Is Scalmalloy® available for commercial use, and are there licensing restrictions?
Can Scalmalloy® be used for critical flight-certified components?
What post-processing is needed to optimize fatigue and surface properties?
What industries benefit most from adopting Scalmalloy® in additive manufacturing?