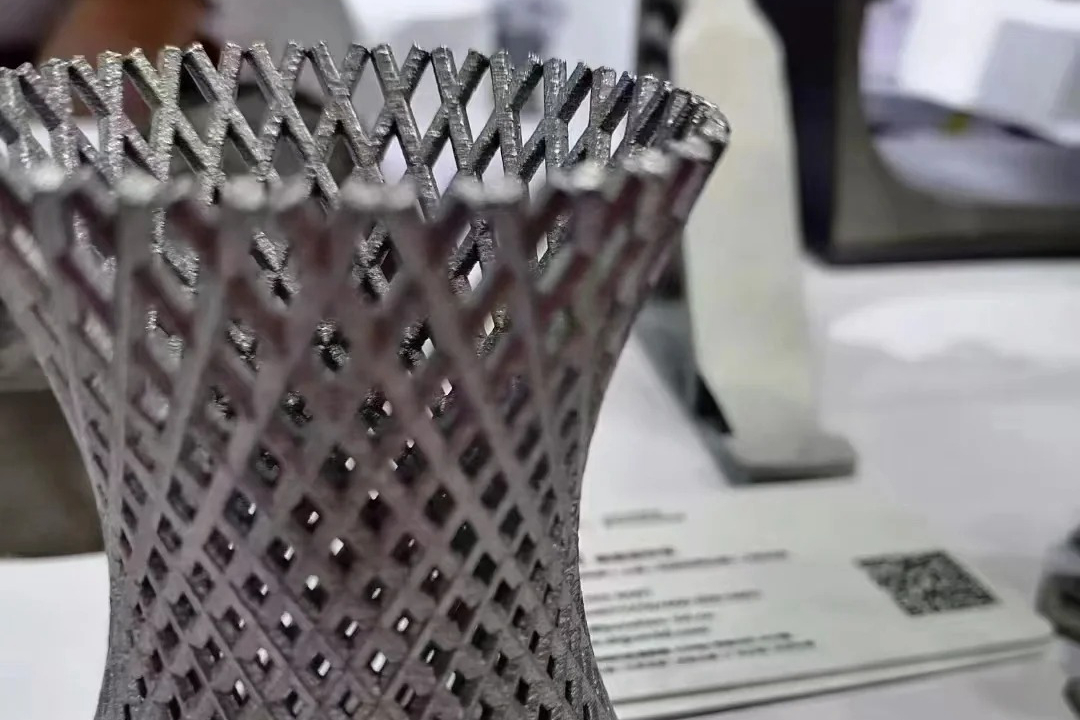
Aluminum AlSi7Mg
Introduction to Aluminum AlSi7Mg for 3D Printing
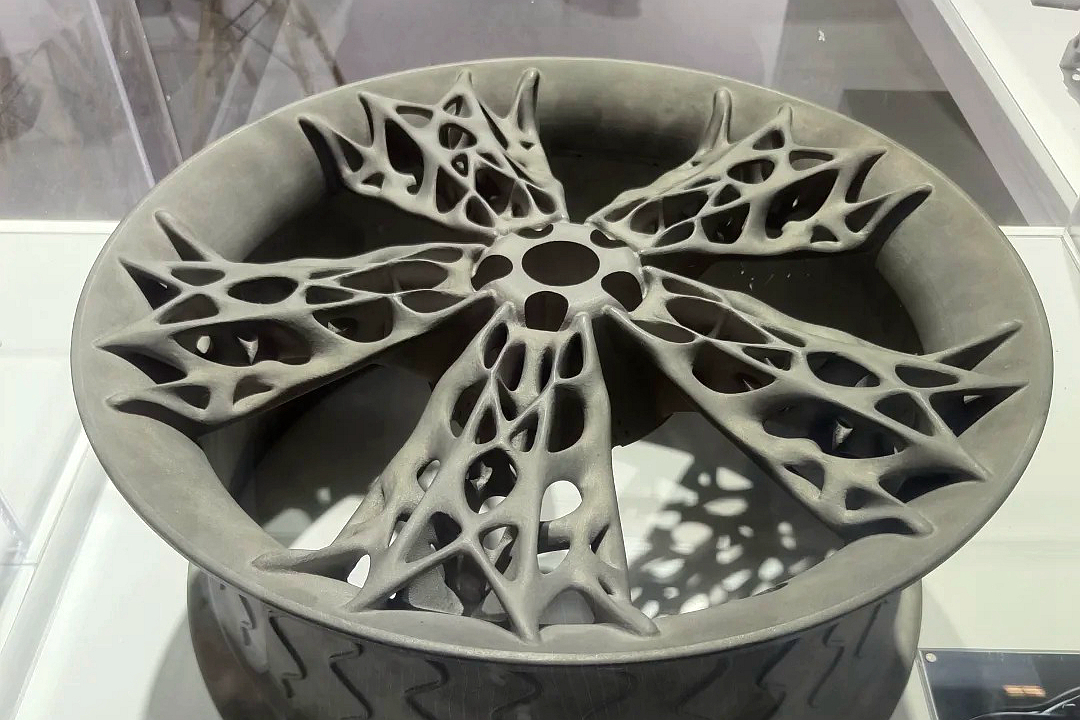
Aluminum AlSi7Mg is a lightweight, castable aluminum alloy with ~7% silicon and ~0.3% magnesium content, offering an excellent balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and castability. It is widely used for thin-walled parts, complex geometries, and lightweight components across the aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) is the preferred technology for 3D printing AlSi7Mg, delivering near-wrought material properties with high accuracy (±0.1 mm) and excellent surface finish for complex functional parts.
International Equivalent Grades of Aluminum AlSi7Mg
Region | Grade Number | Equivalent Designations |
|---|---|---|
Europe | EN AC-42100 | AlSi7Mg |
USA | A356.0 | AlSi7Mg |
China | GB/T 1173 | ZL101A |
Japan | JIS H5302 | AC4A |
Comprehensive Properties of AlSi7Mg (3D Printed)
Property Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Density | 2.68 g/cm³ |
Thermal Conductivity | ~150–170 W/m·K | |
Mechanical | Tensile Strength (as-built) | 310–360 MPa |
Yield Strength | 200–240 MPa | |
Elongation at Break | 4–10% | |
Hardness (Brinell) | 90–110 HB | |
Thermal | Melting Range | ~565–585°C |
Suitable 3D Printing Processes for AlSi7Mg
Process | Typical Density Achieved | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Dimensional Accuracy | Application Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥99% | 8–12 µm | ±0.1 mm | Best for lightweight, thin-walled, and corrosion-resistant parts with excellent cast-like properties |
Selection Criteria for AlSi7Mg 3D Printing
High Castability in Complex Shapes: The eutectic silicon structure makes it excellent for printing parts with thin walls, lattice structures, and complex hollow geometries.
Corrosion Resistance & Surface Quality: Naturally resistant to corrosion and suitable for marine, aerospace, and exposed mechanical assemblies.
Strength vs Weight Optimization: Ideal for components needing medium mechanical strength with lightweighting, such as structural supports and covers.
Cost-Effective Alternative to AlSi10Mg: Comparable strength at lower silicon content, with easier post-machining and improved ductility.
Essential Post-Processing Methods for AlSi7Mg Parts
Heat Treatment (T5 or T6 Aging): Artificial aging enhances yield strength and reduces residual stress for long-term dimensional stability.
CNC Machining: Post-machining enables high-tolerance interfaces (±0.01 mm), thread features, and sealing surfaces.
Anodizing or Coating: Increases wear and corrosion protection—ideal for marine, aerospace, and humid environments.
Surface Polishing or Blasting: Improves surface appearance and feel for customer-facing or aerodynamic components.
Challenges and Solutions in AlSi7Mg 3D Printing
Brittleness in Ultra-Thin Walls: Design minimum wall thickness ≥0.8 mm and use fillets to reduce stress concentration and cracking.
Heat Accumulation in Large Cross-Sections: Segment builds and optimize support to reduce residual stress and potential distortion in thicker geometries.
Oxidation Sensitivity: Print under controlled inert gas (argon) environments with oxygen <100 ppm to prevent powder degradation.
Applications and Industry Case Studies
AlSi7Mg is widely used in:
Aerospace: Lightweight covers, bracketry, fluid channel housings, avionics enclosures.
Automotive: Engine housings, transmission supports, lightweight suspension components.
Marine Equipment: Structural housings, buoyancy systems, saltwater-resistant brackets.
Industrial Machinery: Complex fluid manifolds, pneumatic frames, general-purpose structural parts.
Case Study: A marine systems manufacturer used AlSi7Mg to print saltwater-exposed pump housings with integrated fluid paths. After T5 aging and anodizing, the components passed 1,000-hour salt spray testing with no corrosion and maintained dimensional flatness within ±0.05 mm.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How does AlSi7Mg compare to AlSi10Mg or AlSi12 in mechanical properties?
What industries benefit most from printing AlSi7Mg components?
Can AlSi7Mg parts be anodized or treated for marine environments?
What is the optimal wall thickness and feature size for 3D printed AlSi7Mg?
Are heat treatments necessary to improve the mechanical performance of AlSi7Mg prints?