Aluminum 2024
Introduction to Aluminum 2024 for 3D Printing
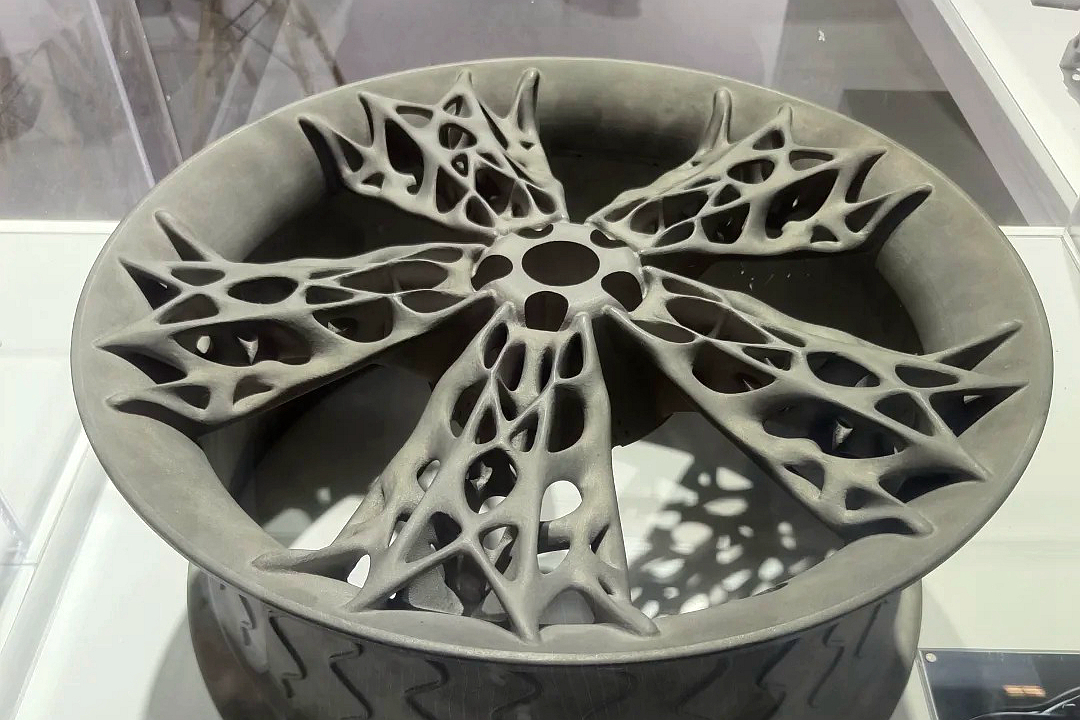
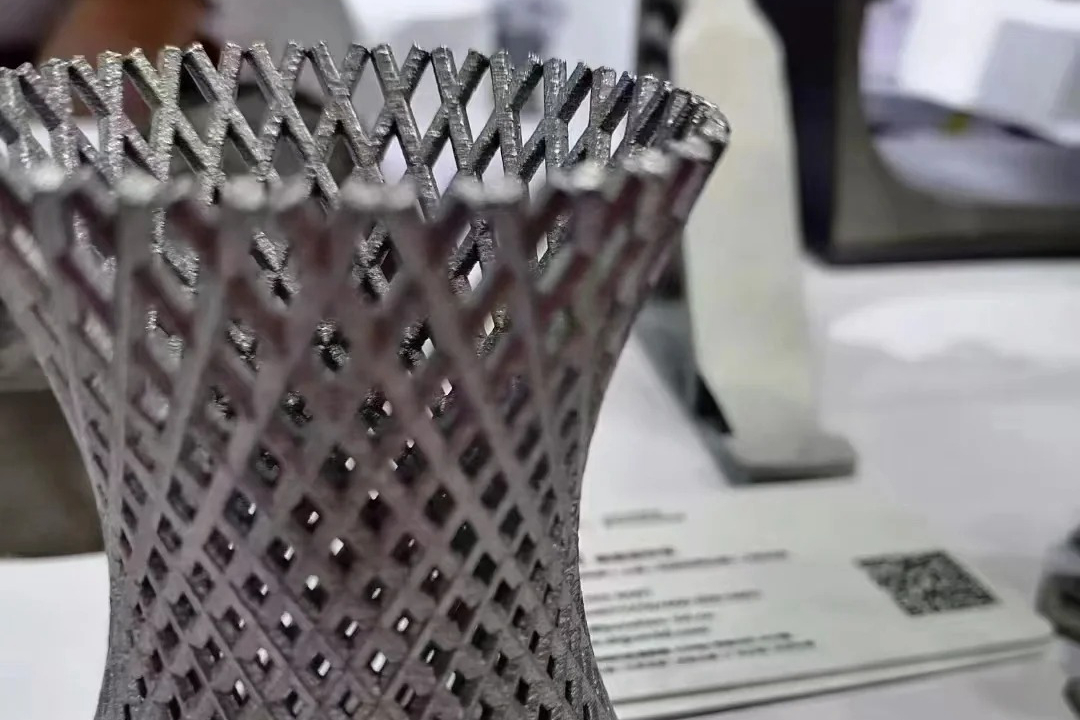
Aluminum 2024 is a high-strength, copper-alloyed aluminum used extensively in aerospace and structural applications. Known for its superior fatigue resistance and excellent machinability, it is commonly used for aircraft skins, fuselage structures, and high-load brackets. Though traditionally not weldable or castable, modern additive manufacturing makes 3D printing Aluminum 2024 possible for lightweight, performance-critical components.
Powder Bed Fusion (PBF) and Directed Energy Deposition (DED) are the primary 3D printing technologies for Aluminum 2024, offering high-density (≥98%) parts with mechanical properties comparable to wrought material.
International Equivalent Grades of Aluminum 2024
Region | Grade Number | Equivalent Designations |
|---|---|---|
USA | AA 2024 | UNS A92024 |
Europe | EN AW-2024 | AlCu4Mg1 |
China | GB/T 3190 | 2A12 |
Japan | JIS H4000 | A2024 |
Comprehensive Properties of Aluminum 2024 (3D Printed)
Property Category | Property | Value |
|---|---|---|
Physical | Density | 2.78 g/cm³ |
Thermal Conductivity | ~120–140 W/m·K | |
Mechanical | Tensile Strength (as-built) | 400–470 MPa |
Yield Strength | 250–320 MPa | |
Elongation at Break | 6–12% | |
Hardness (Brinell) | 110–135 HB | |
Thermal | Melting Point | 500–638°C |
Suitable 3D Printing Processes for Aluminum 2024
Process | Typical Density Achieved | Surface Roughness (Ra) | Dimensional Accuracy | Application Highlights |
|---|---|---|---|---|
≥98% | 8–12 µm | ±0.1 mm | Best for high-load, lightweight aerospace brackets, drone frames, and structural housings | |
≥97% | 20–30 µm | ±0.3 mm | Suitable for large structural components or repair of 2024-based systems |
Selection Criteria for Aluminum 2024 3D Printing
High Fatigue Resistance: Ideal for aerospace and structural components that experience cyclic loading or high vibration.
Excellent Machinability: Easily CNC-machined post-print for precise holes, tight fits, and threading in aerospace assemblies.
Lightweight Load Bearing: Superior strength-to-weight ratio enables efficient lightweighting for flight, motorsport, and robotics parts.
Heat Treatment Compatibility: Supports post-print T6-type aging to enhance strength and mechanical performance.
Essential Post-Processing Methods for Aluminum 2024 Parts
Heat Treatment (T6 Equivalent): Solution heat-treated and artificially aged to boost tensile strength and reduce residual stress.
CNC Machining: Used for final precision features, such as dowel holes, mating faces, and mechanical interfaces.
Anodizing or Chromate Coating: Required for corrosion resistance due to 2024’s copper content; improves wear and durability in exposed environments.
Polishing or Bead Blasting: Improves surface finish and aesthetics for exposed or assembly-facing components.
Challenges and Solutions in Aluminum 2024 3D Printing
Hot Cracking and Fusion Issues: 2024 is crack-prone during fusion; special alloying or modified powder blends are often used in additive manufacturing to reduce defects.
Corrosion Sensitivity: Anodizing or chromate conversion coating is necessary post-print to protect against galvanic corrosion.
Support and Build Strategy Complexity: Requires optimized build orientation and support strategies to control residual stress and shrinkage.
Applications and Industry Case Studies
Aluminum 2024 is widely used in:
Aerospace: Wing spars, seat frame brackets, control linkage arms, and structural fittings.
Motorsports: Suspension mounts, custom brackets, and impact-resistant structural components.
Defense: Lightweight, ruggedized housings, drone frames, and deployable airframes.
Industrial Equipment: Load-bearing parts in robotics, automation, and high-cycle dynamic assemblies.
Case Study: A UAV manufacturer 3D printed custom 2024 alloy motor mounts using PBF. After T6 treatment and surface finishing, the components exceeded fatigue test standards and reduced weight by 35% compared to machined parts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the key benefits of 3D printing Aluminum 2024 versus 6061 or 7075?
Can 2024 aluminum be heat treated after 3D printing to improve strength?
Is Aluminum 2024 suitable for cyclic load or vibration-critical aerospace parts?
What post-processing is needed to prevent corrosion in 2024 parts?
Which industries benefit most from 3D printing high-strength 2024 aluminum components?