How does EDM differ from traditional polishing in achieving mirror finishes?
How EDM Differs from Traditional Polishing in Achieving Mirror Finishes
Principle of Material Removal
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
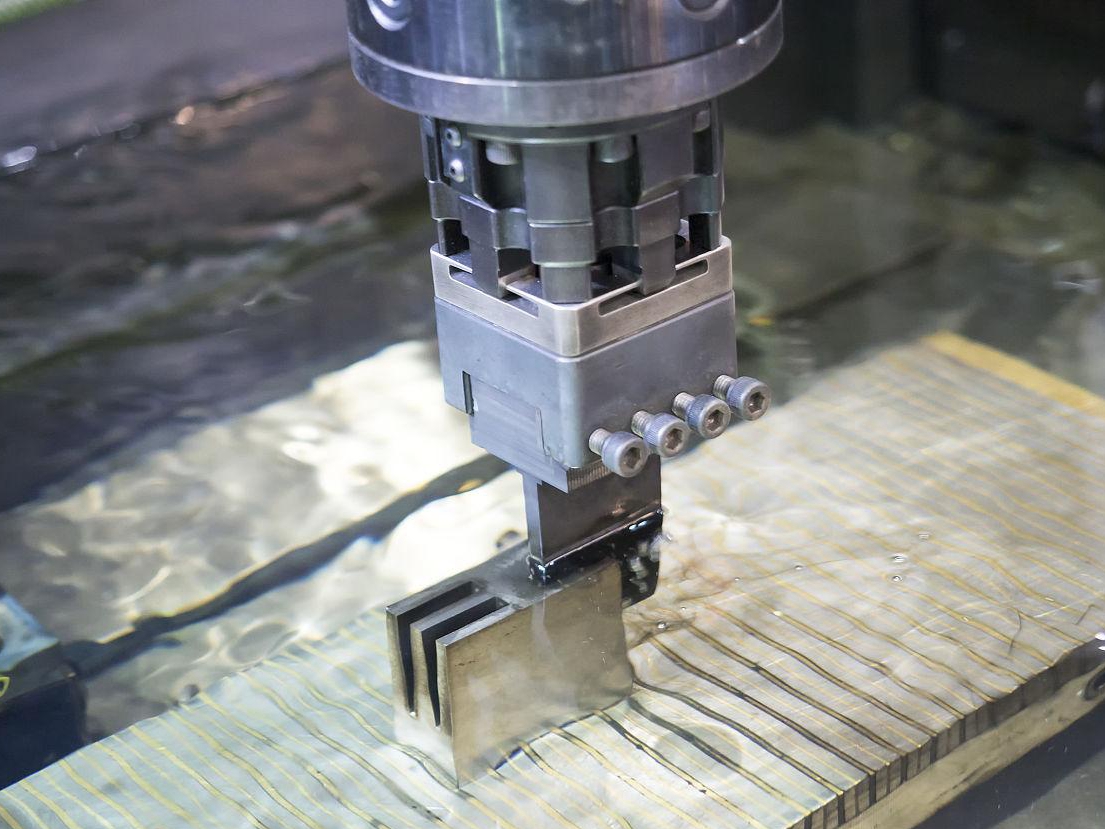
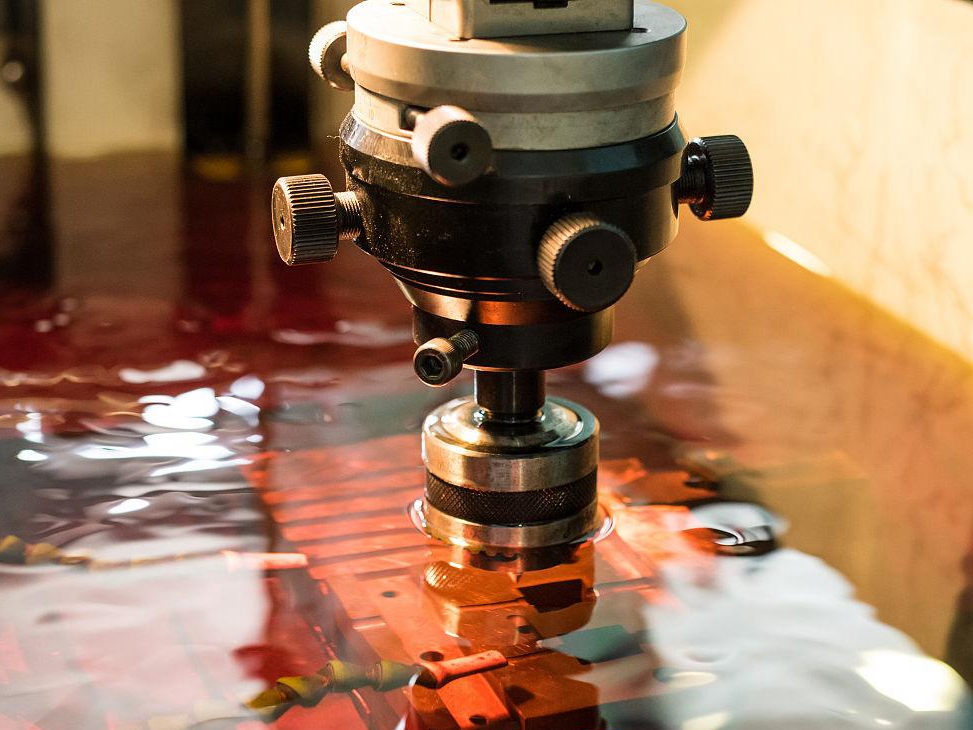
EDM uses controlled electrical discharges to remove material from a conductive workpiece without physical contact. The part is submerged in dielectric fluid, and the material is vaporized and eroded by spark discharges between the tool electrode and the part surface. This allows precise material removal even in hard-to-reach internal geometries, making it ideal for complex metal 3D printed parts such as those built using Selective Laser Melting (SLM) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM).
Traditional Mechanical Polishing
In contrast, traditional polishing relies on abrasive contact using tools like buffing wheels or abrasive pastes. Material is physically removed through friction, which can introduce mechanical stress, deformation, and inconsistency on delicate or complex 3D printed surfaces. This method is less effective for internal features or deep cavities.
Surface Finish Precision and Repeatability
EDM can consistently achieve surface roughness values below Ra 0.2 µm on difficult materials such as Inconel 718, Ti-6Al-4V Grade 5, or Tool Steel H13. Since there’s no tool wear affecting the shape of the electrode, the process maintains uniformity and dimensional accuracy over repeated runs.
Traditional polishing is more operator-dependent and less reproducible, especially on high-precision components. Achieving a consistent mirror finish across batches or complex part features can be labor-intensive and inconsistent.
Geometrical Versatility
EDM excels in processing deep holes, narrow slots, and internal cavities—features common in advanced applications such as turbine blades and conformal cooling channels. It is highly compatible with components produced from hard-to-machine materials like Hastelloy C-276 or Tool Steel M2.
Mechanical polishing is restricted by tool access. It cannot easily reach intricate or internal surfaces, making it unsuitable for many 3D printed or complex geometries.
Thermal and Mechanical Impact
EDM is a non-contact process and induces minimal mechanical stress. With proper dielectric flushing and optimized parameters, thermal damage is minimized. In contrast, polishing generates frictional heat and mechanical forces that may distort thin-walled or fine-featured parts, especially in materials like Ti-6Al-4V ELI (Grade 23) or SUS316L.
Recommended Finishing Services from Neway 3DP
To achieve optimal surface finishes tailored to your part geometry and application, we offer:
EDM Machining Non-contact mirror finishing for complex or high-hardness 3D printed metals.
Electropolishing Ideal for stainless steel and titanium parts, improving corrosion resistance and surface clarity.
Polishing Suitable for accessible and aesthetic surfaces in consumer and medical products.
We select the most suitable method or hybrid finishing strategy based on part material, tolerance requirements, and application needs.