What plastic materials are commonly used in Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
What Plastic Materials Are Commonly Used in Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)?
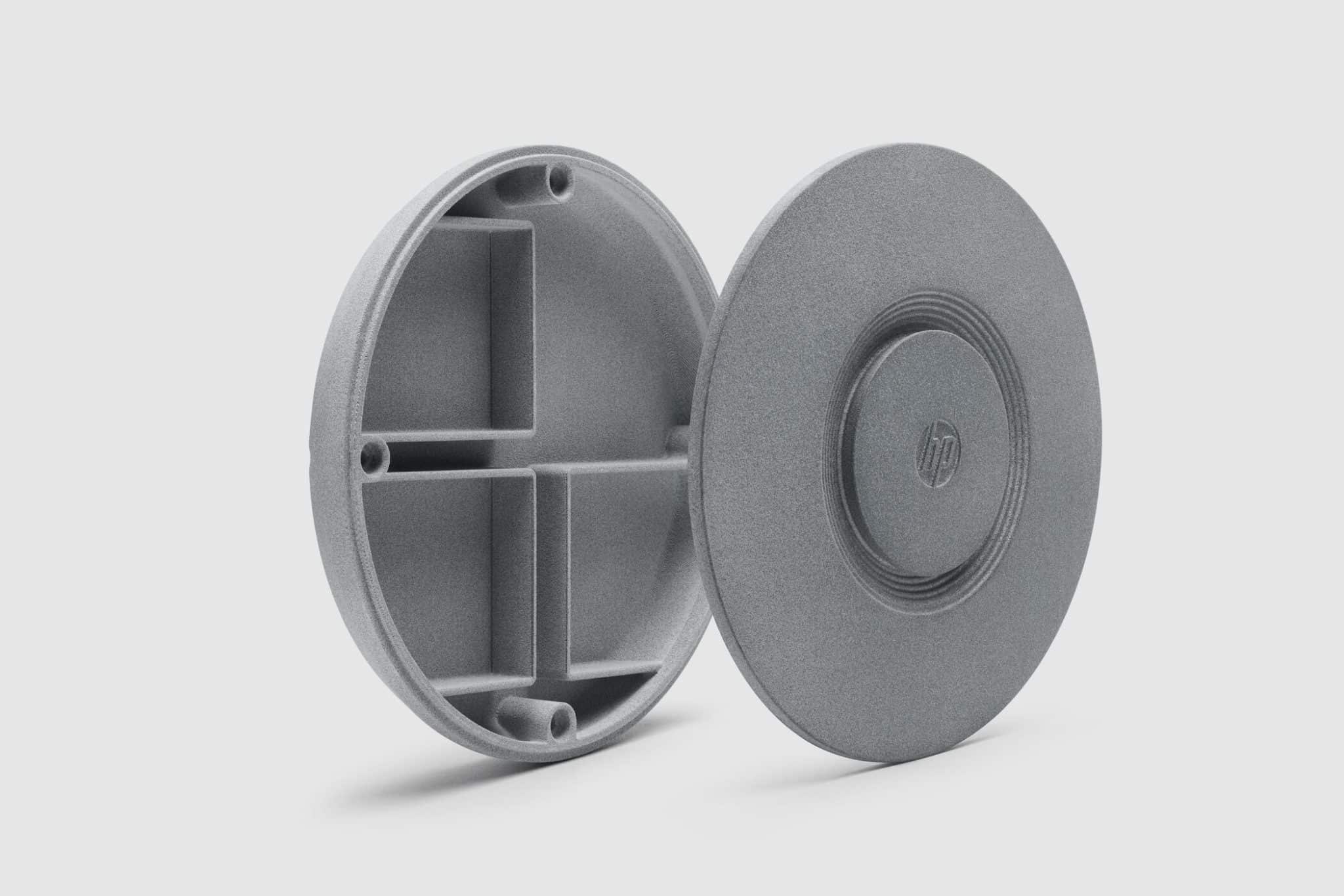
Nylon PA12
Nylon (PA12) is the most widely used material in SLS due to its balanced mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and long-term durability.
Tensile strength: ~48 MPa
Elongation at break: ~20%
Applications: Brackets, housings, snap-fits, fluid system connectors
Glass-Filled Nylon (PA12-GF)
Glass-fiber reinforcement improves stiffness, heat resistance, and dimensional stability.
Tensile modulus: ~3,200 MPa
Applications: Under-hood components, structural panels, load-bearing fixtures
Carbon-Fiber-Filled Nylon
This composite material offers a higher strength-to-weight ratio and low thermal expansion.
Enhanced stiffness and impact resistance
Applications: Jigs, mounts, fixtures, lightweight brackets
Nylon PA11
Derived from renewable castor oil, PA11 offers higher ductility and impact resistance than PA12.
Biocompatible and suitable for chemically aggressive environments
Applications: Prosthetics, flexible connectors, enclosures
Flame-Retardant Nylon
Modified PA12 formulations meet UL94 V-0 ratings for flame resistance.
Ideal for electrical housings and interior automotive parts
Applications: EV connectors, cable ducts, fuse boxes
ESD-Safe Nylon
Electrically conductive additives allow for static-dissipative performance.
Surface resistivity: 10⁶ to 10⁹ ohms
Applications: Electronic packaging, sensor enclosures
Customer-Oriented Solutions and Services
To support plastic SLS applications, we offer:
3D Printing Technologies:
Utilize Plastic 3D Printing powered by SLS for durable, high-performance parts.
Engineering-Grade Materials:
Choose from Nylon PA12, glass-filled, carbon-fiber-filled, or flame-retardant variants to meet strength, thermal, or regulatory demands.
End-Use Application Support:
Explore solutions in automotive, consumer electronics, and medical and healthcare, with available surface finishing and CNC machining.